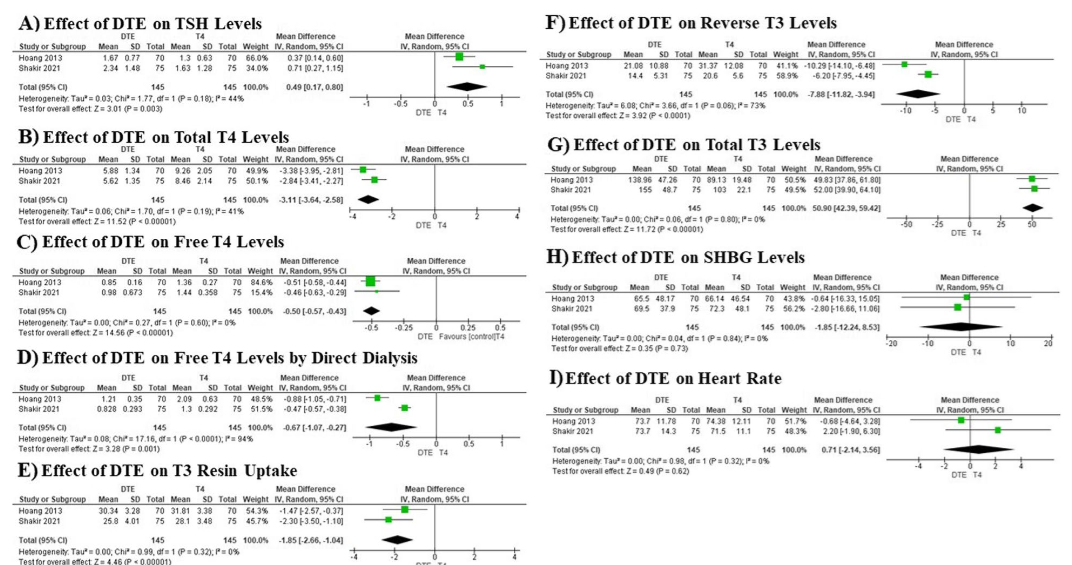
Comment:
A critical takeaway from this meta-analysis is the comparable safety profile of DTE. The data indicates no significant negative impact on key outcomes such as heart rate or lipid profiles when compared to standard T4 monotherapy.
Beyond its safety, a key potential benefit highlighted is its effect on reverse T3 (rT3). Treatment with DTE was shown to result in a significant lowering of rT3 levels. This is a crucial finding, given that rT3 is a biologically inactive hormone that can block active T3 from binding to its receptors.
Summary:
Clinical Bottom Line
This meta-analysis concludes that while combined T4+T3 therapy and desiccated thyroid extract (DTE) significantly alter thyroid hormone levels compared to standard levothyroxine (T4) monotherapy, these changes do not generally translate into significant improvements in most key clinical outcomes, such as lipid profiles, heart rate, or overall quality of life (TSQ-36, BDI scores).
A notable exception is a significant improvement in mental health/well-being seen with combined T4+T3 therapy, as indicated by lower General Health Questionnaire (GHQ-28) scores. DTE treatment resulted in significantly higher TSH and Total T3 levels and lower Total T4 and Free T4 levels, but this did not result in a significant clinical benefit on heart rate, lipid profile, or quality of life measures.
The evidence for both alternative therapies is characterized by high heterogeneity in the included studies for some outcomes, which warrants a personalized treatment approach rather than a blanket recommendation for the broader hypothyroid population.
Results
The meta-analysis was conducted by comparing combined T4+T3 therapy or DTE against T4 monotherapy in hypothyroid patients.
Combined T4+T3 Therapy vs. T4 Monotherapy
-
Thyroid Profile:
-
Total T3 levels were significantly higher with combined therapy.
-
Total T4 and Free T4 levels were significantly lower.
-
TSH levels showed no significant difference.
-
-
Mental Health & Quality of Life:
-
GHQ-28 scores (General Health Questionnaire) were significantly lower, suggesting a benefit in mental health and well-being.
-
TSQ-36 (Thyroid Symptom Questionnaire) and BDI (Beck Depression Inventory) scores showed no significant difference.
-
-
Cardiovascular & Metabolic:
-
Heart Rate, SHBG, and Lipid Profile showed no significant difference.
-
Desiccated Thyroid Extract (DTE) vs. T4 Monotherapy
-
Thyroid Profile:
-
Total T3 levels were significantly higher with DTE.
-
Total T4 and Free T4 levels were significantly lower.
-
TSH levels were modestly but significantly higher.
-
-
Mental Health & Quality of Life:
-
TSQ-36, GHQ-12, and BDI scores showed no significant differences.
-
-
Cardiovascular & Metabolic:
-
Heart Rate, SHBG, and Lipid Profile showed no significant difference.
-
DTE Impact on Reverse T3 (rT3) Levels
The study found a significant lowering of reverse T3 (rT3) levels when patients were treated with Desiccated Thyroid Extract (DTE) compared to T4 monotherapy.
-
Mean Difference: The mean difference in reverse T3 levels was -7.88.
-
Interpretation: A negative mean difference means the DTE group had lower rT3 levels than the T4 monotherapy group. This is consistent with the understanding that therapies containing T3 (like DTE) help shift the balance away from the production of the inactive rT3.
Assertive Critical Appraisal
Certainty of Evidence
The frequent mention of high heterogeneity (e.g., $I^2$ of 96% for Free T4 in T4+T3 comparison) suggests that the certainty of the evidence for those specific outcomes would be downgraded to Moderate or Low. This heterogeneity suggests the results are inconsistent across the included studies, complicating the interpretation of the pooled average effect.
Heterogeneity
Substantial heterogeneity was frequently observed for many key outcomes:
-
Free T4 ($I^2 = 96\%$)
-
TSH ($I^2 = 96\%$)
-
Total Cholesterol ($I^2 = 70\%$)
An $I^2$ of 96% indicates that 96% of the variation across studies is due to real differences in the study populations, methods, or interventions rather than just chance. Such high heterogeneity means the pooled average result should be interpreted with extreme caution.
Publication Bias
The paper does not explicitly state that the authors assessed for publication bias. The authors note that excluding non-English articles introduces language bias and raises concerns about publication bias, which can lead to an overestimation of treatment effects for the reported outcomes.
Risk of Bias in Included Studies
-
For T4+T3 studies: Concerns were prevalent regarding performance and detection bias due to high risk of bias in the blinding of participants and personnel and incomplete outcome data.
-
For DTE studies: All included studies exhibited a low risk of bias in random sequence generation and allocation concealment, suggesting a strong methodological framework for randomization.
Research Objective
The objective of this systematic review and meta-analysis was to rigorously evaluate the effectiveness of combined T4 and T3 therapy or Desiccated Thyroid Extract (DTE), compared to T4 monotherapy in patients with hypothyroidism.2
PICO Framework:
-
P (Population): Patients with hypothyroidism.
-
I (Intervention): Combined T4+T3 therapy or Desiccated Thyroid Extract (DTE).
-
C (Comparator): T4 monotherapy (synthetic levothyroxine).
-
O (Outcomes): Thyroid profile (TSH, T4, T3), lipid profile, heart rate, SHBG, and quality of life metrics (TSQ-36, BDI, GHQ-28).
Study Design
The study is a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs).
-
Search Strategy: Literature search using a Boolean approach was conducted in Embase, Medline/PubMed, and Web of Science up to November 23, 2023.
-
Inclusion Criteria: Strictly limited to RCTs involving combined T4/T3 or DTE versus levothyroxine for primary hypothyroidism in adults (age $\ge 18$ years), published in English.
-
Study Selection: Two independent coauthors conducted the screening and a total of 16 studies were included in the final analysis (2 on DTE and 15 on combined therapy).
Bibliographic Data
-
Title: Evaluating the effectiveness of combined T4 and T3 therapy or desiccated thyroid versus T4 monotherapy in hypothyroidism: a systematic review and meta-analysis
-
Authors: Mahmoud Nassar, Ahmed Hassan, Shrouk Ramadan, Mariam Tarek Desouki, Malak A. Hassan and Ajay Chaudhuri
-
Journal: BMC Endocrine Disorders
-
Year: 2024
-
DOI: 10.1186/s12902-024-01612-6
This AI-generated analysis is for informational and research purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.
Original Article:
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
